In an era where computers have become integral to our daily lives, it's not just about how powerful your machine is; it's also about how effectively you can keep it cool. Heat is the arch-nemesis of computers, capable of wreaking havoc on their performance and longevity. But fear not, for the world of cooling systems has evolved significantly to combat this nemesis. In this in-depth guide, we'll dive into the intricate realm of computer cooling, exploring the various types of cooling systems, how they function, and which one is best suited for your computing needs.
The Vital Role of Cooling Systems
Before we delve into the specifics of cooling systems, it's essential to understand why they are so crucial for your computer. Whether you use your computer for gaming, content creation, or everyday tasks, your CPU and GPU work tirelessly, generating a substantial amount of heat in the process. This heat, if left unchecked, can lead to several problems, including:
Reduced Performance: Overheating can lead to thermal throttling, where your CPU and GPU slow down to prevent damage, resulting in reduced performance.
Component Damage: Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can damage computer components, particularly the CPU and GPU.
System Instability: Overheating can cause system crashes, leading to lost work or unsaved game progress.
Shortened Lifespan: High operating temperatures can significantly shorten the lifespan of your components.
To combat these issues, cooling systems play a pivotal role in maintaining your computer's temperature within safe operating limits, ensuring a smoother and more efficient performance.
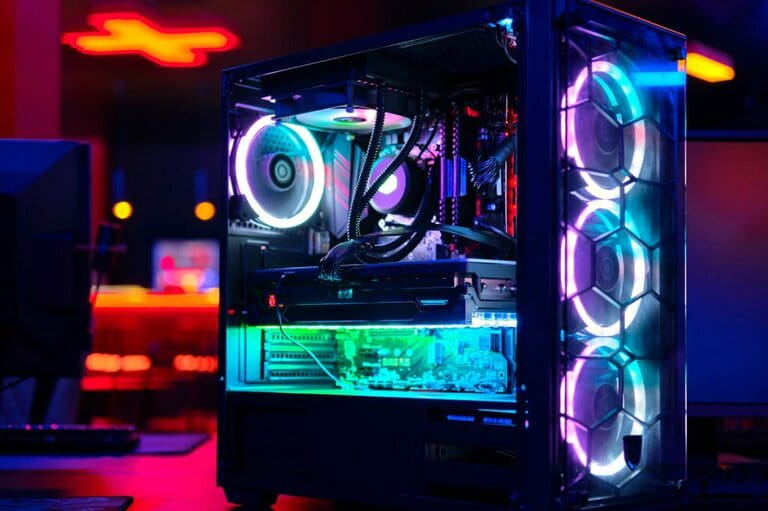

Different Types of Cooling Systems
Now, let's explore the world of cooling systems and the various types available to cater to different computing needs:
1. Air Cooling
How It Works: Air cooling is the most prevalent and budget-friendly cooling solution. It relies on the principles of convection and conduction to dissipate heat from your CPU and GPU. An air cooler typically consists of a heat sink and a fan. The heat sink absorbs heat from the CPU or GPU, and the fan blows cool air over the heat sink's fins to dissipate that heat.
Pros:
- Affordable: Air coolers are cost-effective and readily available.
- Low Maintenance: They require minimal maintenance and are relatively easy to install.
- Effectiveness: Air coolers are suitable for moderate to high workloads and keep your components at acceptable temperatures.
Cons:
- Limited Cooling Capacity: Air coolers may struggle to handle the heat generated by high-end CPUs and GPUs, especially in extreme overclocking scenarios.
- Noise Levels: While many modern air coolers are designed to be quiet, some can generate more noise compared to liquid cooling solutions.
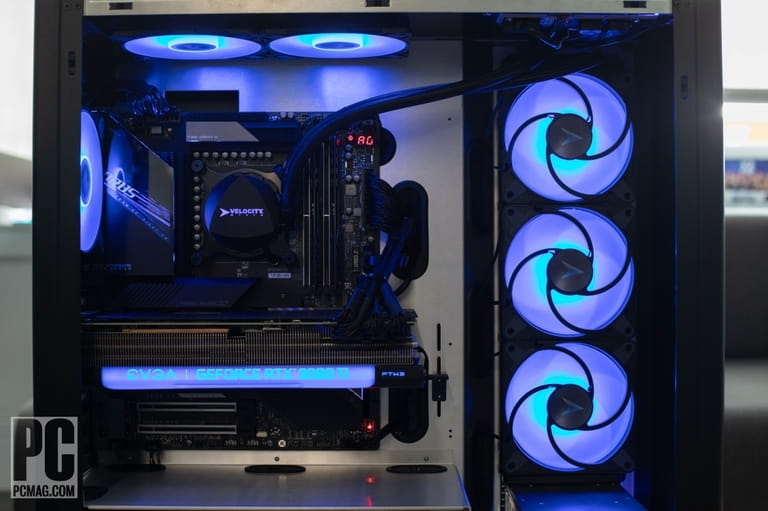

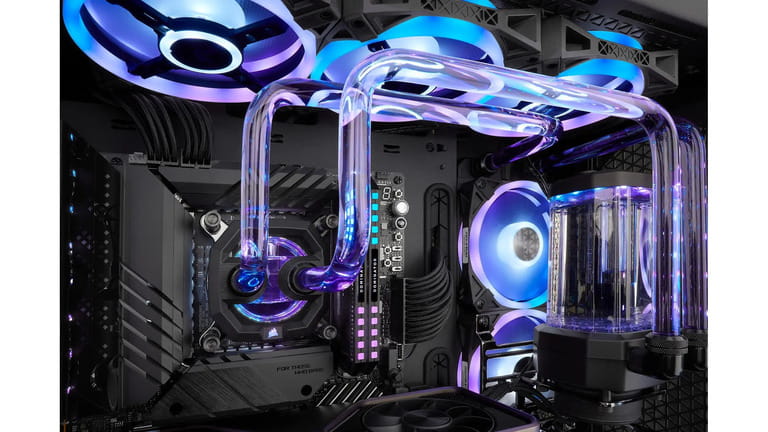
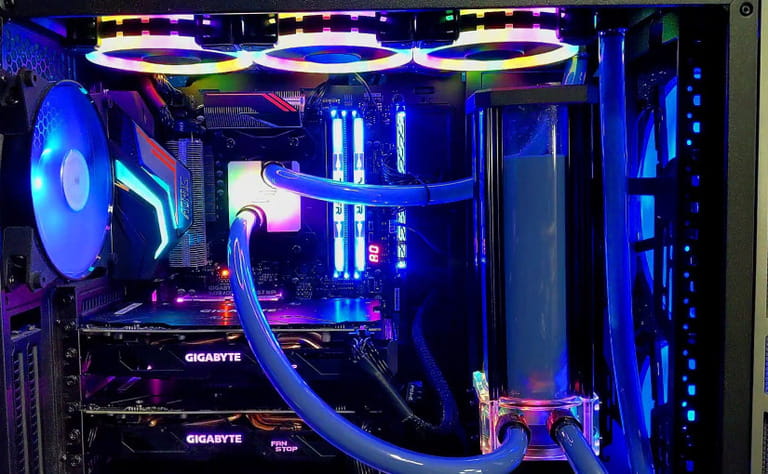
2. Liquid Cooling
How It Works: Liquid cooling, often referred to as water cooling, employs a closed-loop system to circulate a coolant (usually a mix of water and additives) through a block attached to the CPU and/or GPU. The heated coolant is then pumped to a radiator, where fans dissipate the heat. The now-cooled coolant returns to the CPU or GPU block to continue the cycle.
Pros:
- Excellent Cooling Performance: Liquid cooling systems are known for their superior heat dissipation, making them ideal for high-end systems and overclocking.
- Low Noise: Liquid cooling systems tend to be quieter than their air-cooled counterparts.
- Aesthetics: Liquid cooling systems often come with customizable RGB lighting, adding a touch of flair to your rig.
Cons:
- Cost: Liquid cooling systems are more expensive than air cooling solutions, making them less accessible for budget builds.
- Complex Installation and Maintenance: Setting up a liquid cooling system can be more challenging, and they require regular maintenance to prevent issues like coolant leakage.

3. Peltier (Thermoelectric) Cooling
How It Works: Peltier, or thermoelectric, coolers use the Peltier effect to transfer heat from one side of the device to the other. They are often used in combination with traditional air or liquid cooling solutions. A Peltier cooler is positioned between the CPU/GPU and the heatsink. By applying an electrical current, it pumps heat away from the component.
Pros:
- Precise Temperature Control: Peltier coolers can precisely regulate temperatures.
- Effective Heat Reduction: They excel at reducing heat, enhancing the cooling capacity of existing solutions.
Cons:
- Cost and Complexity: Peltier coolers can be expensive, and integrating them into a cooling system can be complex.
- Power Requirements: Peltier coolers require a separate power source, adding complexity to your system.

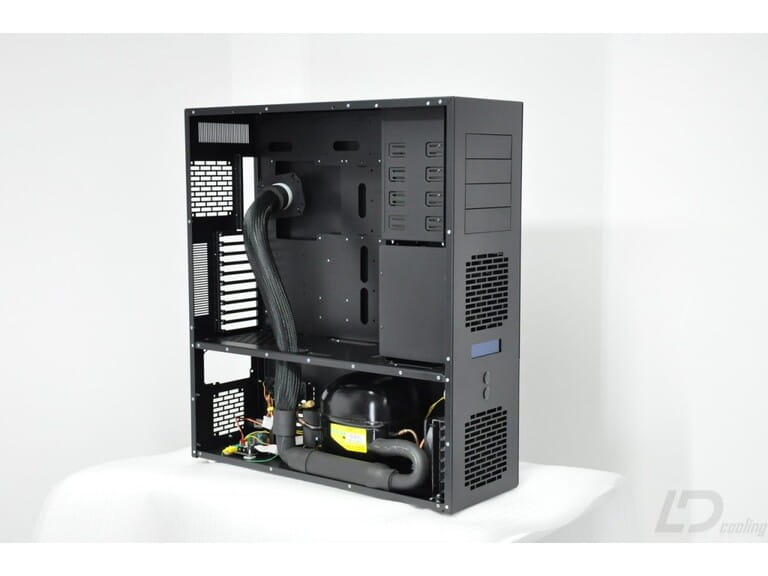
4. Phase-Change Cooling
How It Works: Phase-change cooling systems use a refrigeration cycle to keep the CPU or GPU at low temperatures. These systems are popular in extreme overclocking scenarios, where maintaining the lowest possible temperature is crucial.
Pros:
- Exceptional Cooling Capacity: Phase-change cooling systems are capable of cooling components to sub-zero temperatures, ideal for extreme overclocking.
- Stable Temperatures: They offer precise and stable temperature control.
Cons:
- Cost and Complexity: Phase-change systems are among the most expensive and complex cooling solutions available.
- Maintenance and Setup: Operating and maintaining these systems require a high level of expertise.

5. Passive Cooling
How It Works: Passive cooling relies on heat sinks and convection to dissipate heat from components. It's primarily used in low-power, fanless computers and certain graphics cards. Passive coolers are made of materials with high thermal conductivity to passively transfer heat away.
Pros:
- Silent Operation: Passive cooling is entirely silent since it doesn't rely on fans.
- Energy Efficient: There's no additional energy consumption associated with passive cooling.
Cons:
- Limited to Low-Power Components: Passive cooling is suitable for low-power CPUs and GPUs but is inadequate for high-performance systems.
- Heat Constraints: Passive coolers may struggle to maintain temperatures within safe limits when subjected to high workloads.
Choosing the Right Cooling System
Selecting the appropriate cooling system for your computer depends on a combination of factors, including the components you have, your budget, your use case, and your personal preferences:
1. CPU and GPU: High-performance CPUs and GPUs generate more heat, so select a cooling solution capable of handling that additional thermal load.
2. Overclocking: If you plan to overclock your components, ensure that your chosen cooling system can efficiently dissipate the extra heat generated.
3. Form Factor: Ensure that your cooling solution fits within your computer case's physical constraints.
4. Budget: Cooling solutions vary significantly in price, so consider your budget when making a choice.
Maintaining Your Cooling System
Regular maintenance is essential to keep your cooling system running efficiently and prolong its lifespan. Here are some tips for maintenance:
Dust Management: Dust can accumulate on fans and heatsinks, reducing their efficiency. Regularly clean these components to prevent overheating.
Liquid Cooling Checks: If you have a liquid cooling system, check for leaks and ensure that the coolant is at the appropriate levels.
Monitoring Temperatures: Use software to monitor your component temperatures. Sudden temperature spikes or unusual noises could indicate an issue.
Conclusion
In the ever-evolving world of computer hardware, effective cooling is paramount. It's not just about aesthetics or achieving impressive overclocking feats; it's about safeguarding your computer's performance and longevity. Whether you opt for the cost-effective air cooling, the high-performance liquid cooling, or even venture into the realm of extreme cooling solutions like Peltier, phase-change, or passive cooling, understanding the different types of cooling systems and their applications is your first step toward ensuring that your computer stays cool, quiet, and efficient for years to come.











