The power supply is one of the underrated components in a gaming system. If they are the first users, they will face many difficulties in researching and choosing the best power supply for their needs.
There are simply hundreds of power supplies on the market and many factors at play. The power supply for a PC is the main part of a game console or any PC. It is the job of the power supply unit to ensure that the PC components receive a clean and constant current. So how to choose a power supply for a PC, let's find out below.
What is a power supply for a PC?
A power supply or PSU is a component that converts the alternating current coming from a wall outlet into the direct current that a PC's components require to function.
Unlike home appliances, PC components require a constant, steady DC to function properly. Make sure power is available, current is cleanly and efficiently converted from AC to DC and then supplied to the specific components that need it. While power may not contribute directly to the PC's aesthetics or performance, without power the PC won't even WORK. So Power Supply is a core and essential part of a PC that needs proper attention and care.
What is 80 PLUS certification?
When you search for power supplies, you'll see many with the 80 PLUS certification label. 80 Plus is a certification program that manufacturers can use to provide assurances that their power supplies will meet certain efficiency requirements. In addition, the 80 PLUS comes in a variety of levels, from certified basic to Titanium, and the power supply is also evaluated by independent laboratories to provide performance levels for your 115-volt electrical systems. consumption.
1. Size of power supply
Overall, PC sizes can range from very large to relatively small. As a result, you can't have a standard power supply size to service many capabilities. The PSU form factor gives manufacturers (case manufacturers, OEM manufacturers, etc.) freedom when it comes to designing new things.
Designing a small PC case knowing that the power source will take up nearly half of the case volume. Surely there won't be much room left for much else.
Nearly the power supply form factor either addresses size or power requirements or both. Below are a few of the popular PSU form factors you'll find on the market:
ATX
This multiplier is most common for desktop computers. When buying a power supply for a regular PC or in some cases a compact PC, this is the form factor.
SFX (Small)
If you're building a compact Mini-ITX system, you'll see a lot of cases where an SFX power supply is required. Modern SFX PSUs power high-end systems with ease.
LFX (Low Profile)
This form factor for compact, low-profile computers with power requirements typically ranges from 180W to 260W (v1.1).
FlexATX
It is not standard for PSU length and fan placement. These PSUs are only used by OEMs like Dell and HP, but they are also sometimes used in rack server chassis.
TFX (Thin)
This is another type of power supply for more compact cases but is specially designed for 'thin' cases.
ATX vs. ATX12V
There is a difference between ATX and ATX12V.
Intel recently developed the ATX form factor and power standard in 1995 to standardize power supplies for computers. The ATX12V is the latest iteration of that ATX specification (whose update is version 2.53, released June 2020).
2. Modular and semi-modular PSU
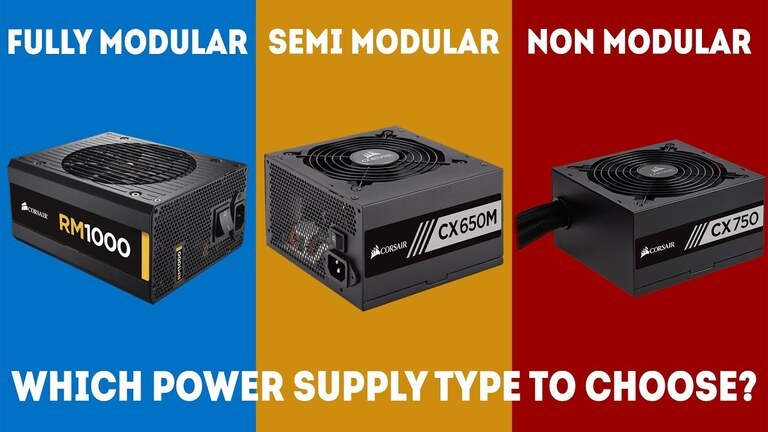

The module is one of the parts you need to provide for your power supply purchase. Most PSUs come with a cord already permanently attached to the power source. So how is it here?
Some places won't use all the cables that come with the power supply. Here you only need a few, and unused cords will be an eyesore when tucked into the dark side of the case.
Furthermore, some people prefer to use only the power cable they need, whereas a modular power supply can help reduce the clutter of wires inside the PC.
3. Quiet or fanless power supply equipment

Removing the fan from the PSU will make it silent/noisy, but be aware that fanless and silent power supplies are not the same thing.
While a fanless power supply is silent due to fan irritation, a quiet power supply just minimizes fan noise as much as possible.
Some companies will use near-silent fans even when handling high loads. However, there are still some that will only use the fan when the PC starts pulling more than the set power threshold,
like Corsair's RM series offers a Non-RPM Fan Mode that ensures the fan spins only at high loads. These power supplies have a range from 450 Watts to 1000W.
Furthermore, a fanless power supply can't deliver too much power because the components would be too hot to handle without a fan circulating cool air, as Seasonic will offer some high-powered and fanless PSUs. is 500W on a fanless PX-500 Prime Module device.
As for the workstation, there is no fan but the load is too high and continuous enough to be eliminated. However, when the workstation is on a desk, a quiet PSU will help reduce system noise when idle.
4. Rails in a power supply unit

Rails are the paths/conductors inside the power supply that carry electricity. According to the ATX12V standard, the power supply by default provides the following rails:
3.3V: used by RAM, but its use is slowly disappearing as motherboards now have a VRM to power the memory, drawn from the 12V rail. This rail also powers the M.2 SSD.
5V: used to power SATA devices such as hard drives, optical drives, PCI add-in cards, USB
5Vsb (standby)
-12V: no longer used.
12V provides power for CPU, GPU, other PCIe add-in cards, and fans.
Thereby, each of these rails supplies power to different parts of the system. In it, the 12V rail does all the heavy lifting, powering the CPU and GPU, among other things.
5. Cable
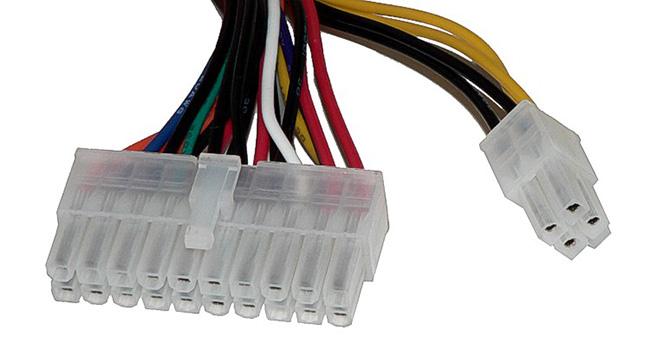
Usually bundled with the PSU can give a good assessment of the overall quality of the PSU.
Make sure that the PSU comes with the necessary cables for the system. Then review your graphics card and check how many PCIe Power connectors it requires.
In addition, you should also take into account all SATA and MOLEX-enabled accessories inside the system and make sure that the PSU provides enough connectors and cables for them. The number and type of cables that come with the PSU are also listed on the product page as well as on the PSU's packaging.
Thereby you can judge the quality of the PSU by the included cables. If a very high-quality PSU, like the Corsair RM850x, comes with multiple 8-pin PCIe Connectors (3 in the case of the 850x). Various ATX 12V and SATA connections will also be included.
These additional cables may not be included in the low-priced, low-quality models. Black or flat cables with sleeves also tend to be included with high-end models.
6. Aesthetics
Add to your notebook the criteria for judging a PSU by its appearance. You should look at the outer shell of the PSU. With low-priced, low-quality equipment that may not even be powder coated and a cheap metallic look. A good quality PSU includes flat, black cables and connectors, improving the overall aesthetic of the system. Cheaper PSUs include sleeveless multicolored wiring, which can easily spoil the look of a build.
While not positive on solid tests of the PSU's quality, it is an indicator of performance.
In general, manufacturers choose to save a few cents by skipping the powder coating; a lot of corners have been cut more than with actual components. Therefore, spend a lot to have a good product.
7. Connector
The power source will not work when it is not connected and provides power to all the components in the PC. It should therefore have all the required connector types.
The main connector that powers the motherboard should be the first connector to consider. And it has two types, 20 pins, and 24 pins. With the latter being common, it's likely your power supply will offer both options. You just need to check for being sure.
The second is the processor power connector, which is available in 4-pin and 8-pin versions. Similar to the main power connector, many modern motherboards have switched to a larger format.
In general, the most frequently used power connectors are 4-pin Molex connectors. It is used for many components including old hard drives, optical drives, fans, and several other devices.
The SATA components have their own SATA power connector and can also use a Molex to SATA adapter if they run out. Furthermore, you can use splitter cables to increase the number of connected components, but limit the power supply's upper limit.
Conclusion
There's indeed a lot to choosing a power supply and how to put together a new PC. However, it takes some time to ensure a reliable power supply to PCcomponents. This will save you a huge amount of time in the long run, and it will support your PC better and be more efficient than machines.











